-
Innovative Financing Workshop on October 4, 2023 in La Vista, NE
Build America Center is supporting Metropolitan Area Planning Agency (MAPA) and the Nebraska Department of Transportation to organize an Innovative Financing Workshop from noon to 5 pm on Wednesday, October 4th at the Embassy Suites in La Vista, Nebraska. Register Now! Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), and the Build America Bureau officials will provide an overview of the tools, expertise and financing available to help the transportation…
-
3 Ps in a Pod
Join Deputy Editor Jonathan Davies of the P3 Bulletin and Partnerships Bulletin as he talks with the Dr Qingbin Cui on how the Build America Center is helping to build the next wave of P3s.
-
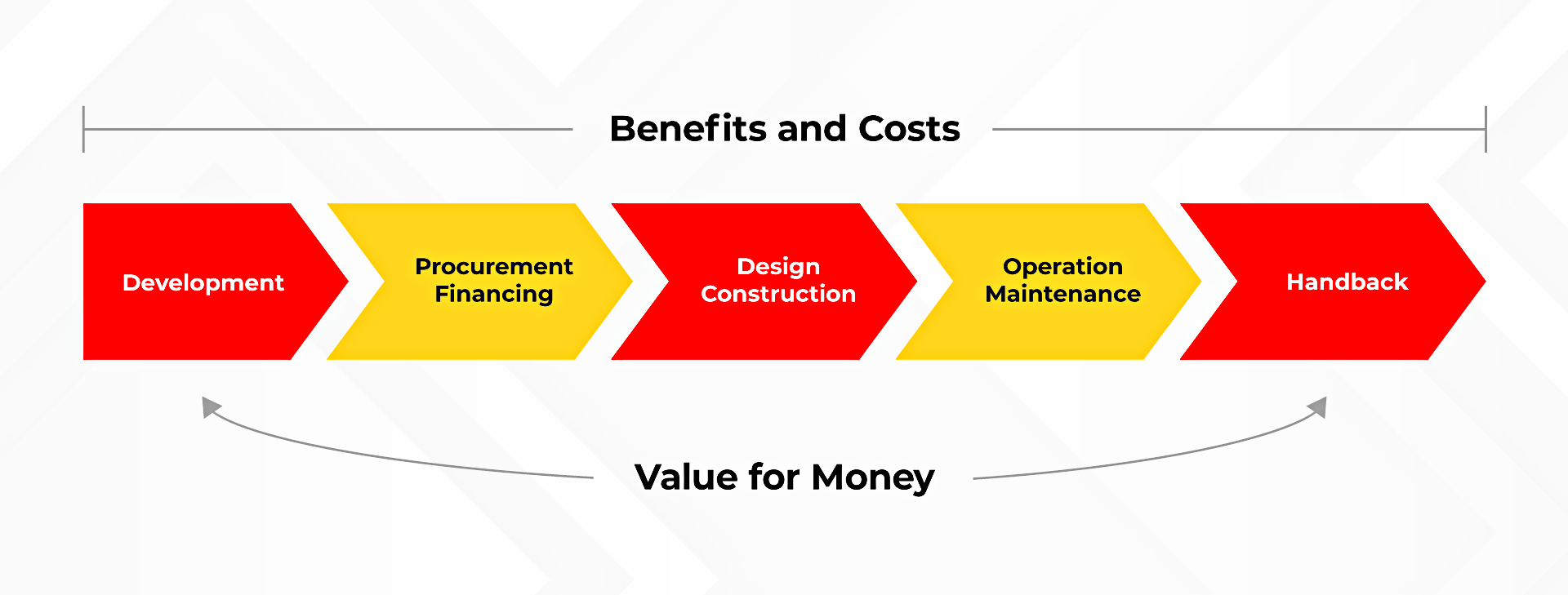
Value for Money Analysis Principles
The Build America Center (BAC) is working to make it a bit easier for agencies to fulfill the Value for Money (VfM) analysis requirement when applying for Federal funding and financing programs included in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA). Sections 11508 and 70701 of the IIJA require a VfM analysis for specific categories…
-
ARTBA P3 Conference’s Special Session: New Ways to Help Build America
The Build America Center (BAC) was the topic of a special session during the 34th Annual ARTBA Public-Private Partnerships (P3) in Transportation Conference held in August. The “New Ways to Help Build America” session featured Dr. Qingbin Cui, Professor of Civil Engineering at the University of Maryland and Director of the Build America Center; Sam…
-
Technical Assistance to Apply for Federal Grants
The Build America Center has the knowledge and resources to provide state and local agencies, MPOs and tribal governments with the technical assistance and support they need so they can apply for Federal Grants to support their local infrastructure projects. Since its inception in April 2022, the BAC has assisted numerous counties, cities and MPOs…
-
UMD to Help Guide Implementation of Infrastructure Law
A historic opportunity exists for states and the nation as a whole to make urgently needed improvements to transportation infrastructure, according to speakers and panelists at the Build Infrastructure Better Symposium, held at the University of Maryland (UMD) on Monday (April 11). The symposium, which featured two expert panel sessions, doubled as the official launch…
-
State and Local Legislation
In order to utilize certain types of transportation funding mechanisms or finance programs, state and local governments must first enact enabling legislation to create the tool or program and to govern the way it works. State legislation also governs the implementation of certain Federal programs. This section of the BATIC Institute website provides overviews of…
-
Federal Legislation
Overview The Federal transportation program is the accumulation of legislative actions focusing on Federal funding, regulation, and other aspects of the nation’s surface transportation systems and their administration. Legislation is updated on a periodic basis, with some updates focused on programmatic areas, some allocating funds, and others doing both. The program has evolved through successive…
-
Other Finance Mechanisms
Two mechanisms for a public agency to compensate a private entity for their project responsibilities (design, construction, finance, operations and/or maintenance) under a concession arrangement are availability payments and shadow tolls. Availability Payments Availability payments are made to a private concessionaire by a public project sponsor based on project milestones or facility performance standards in…
-
Mechanisms to Leverage Federal Aid
Federal-aid fund management tools are designed to provide states with greater flexibility in managing Federal-aid highway funds. Typically state and local governments must provide 20 percent of the funding for projects benefiting from Federal aid. The principal objective of the management techniques described here is to ease restrictions on the timing of obligations and reimbursements…